
ChatGPT Has Changed Digital Literacies
The Introduction Of ChatGPT & The Effects It Has On Contemporary Digital Literacies
The world has changed since the first introduction of Artificial Intelligence, however, when this happened in 1951, Christopher Strachey's AI program was a harmless machine that could compete in a game of checkers, at a rather slow speed. If one compares this to the AI program of today referred to as ChatGPT, it is clear that there is a drastic difference. The idea behind ChatGPT might not be new, but contemporary innovations and the help of this type of AI program have resulted in altering everyone's daily lives. This change offers a challenging future for everyone who is affected. In addition, the people who are affected by this change need to read and write in a whole new manner, because their digital literacies is challenged. In other words, the contemporary forms of technological innovations are bringing more solutions to society, but they also carry some problems with them.
Introduction
ChatGPT made a breakthrough in November 2022. The program is considered an artificial intelligence (AI) chatbot which was created by Open AI (Hughes, 2023). The main aim of ChatGPT is to create responses, which have demonstrated detailed and very accurate answers across the complete realm of knowledge (Hughes, 2023). This program was so good that it had the whole world in a chokehold to the point that most institutions had to reevaluate their manners of functioning. This is because ChatGPT could do its job better, faster and more accurately.
Especially in academia, ChatGPT has had a rather negative impact on students. Students have decided to abuse the tool to generate essays and other answers for them that they could use in their studies. It was therefore important for educational institutions to come together and find solutions to combat this issue. But also people who have worked first-hand with AI programs such as Geoffrey Hinton have raised their concerns regarding this type of machine. Since ChatGPT is not the only AI program that is being developed, Hinton has claimed that there is a formidable tech race (Kleinman & Vallance, 2023). Other companies such as Google and Microsoft are also in search to construct a program that will be similar to what ChatGPT does. Hinton is therefore worried that there are not enough regulations regarding these new tools (Kleinman & Vallance, 2023).
Figure 1. ChatGPT - a handy but dangerous tool.
In this essay, the main aim is to scrutinize the impact ChatGPT has on the digital literacies of normal human beings. This is done first by reviewing the literature to suggest what the issues are in relation towards digital literacies and the possible effects they have. The video by Bloomaert speaking on Old vs New media, the book by Doug Belshaw and the short article by Gunther Kress will be used to describe the problems. Second, the analysis will aid in explaining the relevant issues that have been brought on through AI programs such as ChatGPT. The articles that will be used to describe this phenomenon are by Maastricht University and BBC. Third in the discussion part, there will be examples suggested that relate to the problem of the AI system. One less harmful example is that of Julia Koopman who is a digital content creator and who showcases how she lets her life be controlled by AI, specifically ChatGPT. The other example illustrates the bigger problem regarding ChatGPT, which deals with students who used the chatbot for their essays and were caught. In the end, the conclusion summarises the main points and suggests possible solutions for the future.
Background Information
According to Blommaert (2020), the introduction of new media causes issues, which have come to rise every time contemporary devices are put on the market and fade out of the old media. This is because some view the new as scary and that it apparently brings on challenging changes (Blommaert, 2020). For example, Blommaert (2020) mentions the issues that appeared when the radio was introduced as a new media. It challenged the knowledge that the public was receiving because more people could get a hold of the radio which meant that more people could be told new information faster. This information could not be fact-checked as thoroughly, which caused misinformation to travel faster (Blommaert, 2020). Blommaert (2020), says that there is a common belief regarding new media, which is that most consider it to disrupt the economy of knowledge.
ChatGPT is one of the new media that have been introduced in the 21st century. This type of new media and others such as social media, have caused a drastic change in the way the globe receives information and communicates knowledge. It could be therefore suggested that ChatGPT is causing issues in the economy of knowledge, as a new media of the century. Blommaert (2020) has indicated that when new media is introduced, citizens must improve their digital literacies to adapt to the new media adequately. Also here it is plausible to conclude that through the introduction of ChatGPT, citizens are required to upgrade their digital literacy knowledge.
However, it is vital to reflect on what digital literacies is for the new user to be able to operate ChatGPT. According to Belshaw (2014), digital literacies can be understood on a spectrum, because it entails more than just reading and writing. Digital literacies refer to the social aspects of a person (Belshaw, 2014). It is a manner of the person being able to communicate ‘tool-knowledge’ and ‘content-knowledge’ (Belshaw, 2014). Belshaw (2014) states that a person is only able to communicate this on different levels. This means that there cannot be a proper definition for digital literacies, since everyone has a different base of knowledge about it (Belshaw, 2014). However, Belshaw (2014) was able to redefine what digital literacies entails, which is that it includes technology and practices of cognitive activity. It is therefore important to keep a loser definition for digital literacies because it offers to accurately describe each individual person's literacy levels, states Belshaw (2014). Belshaw (2014) concludes, thus that digital literacies have more than one rule and should always apply their plural meaning.
"Literacy is the term to use when we make messages using letters as the means of recording that message" (Kress, 2004, pg. 1)
The distinct modes that make up digital literacies were also reviewed by Kress (2004). He indicated that there will be meaning lost when people continuously encounter new forms of literacy (Kress, 2004). According to Kress (2004), there is a link between “literacy and communicative practices to social outcomes and the ability of individuals to make and disseminate meaning in a social context” and urges individuals to make changes as the world is changing. His writing focuses on how text is increasingly becoming more image-like, however, the present issue is ChatGPT and how it is a chatbot that offers answers to a person. What one can take away from Kress's (2004) writing is that the world needs to rearrange the meaning of this sort of tool. He focuses on literacy multimodal forms, which could be applied here too (Kress, 2004). It could be suggested that in order for a person to be digitally literate enough, they are required to increase their skills to understand the meaning. In this sense, this would indicate the fact that a person is required to evaluate their knowledge regarding ChatGPT to be fully digital literary enough to use the chatbot accordingly.
Analysis
In a news article titled “ChatGPT and studying it, don’t abuse it” by Maastricht University the problems surrounding the increase of AI programs were put forward (UM-News, 2023). According to Maastricht University, ChatGPT has not been absolutely correct and sometimes it brings up nonsense, but it is believed that it will improve as long as people actively send in feedback (UM-News, 2023). This will result in the AI system updating and advancing over time (UM-News, 2023).
The main objective of the article was to scrutinise strategies by Walter Jansen, from the UM’s Centre for Teaching & Learning EDLAB, and Peter Vermeer, chair of the Committee of Boards of Examiners (UM-News, 2023). They both argued to “safeguard the quality of education” while using appropriate tools to understand the functions of AI programs (UM-News, 2023). The two academics believe that ChatGPT is a tool that is continuously evolving. They also tackled the difficulties of AI systems which deal with students cheating on their essays. According to Jansen and Vermeer, the one solution should be to revert back to “traditional exams with pen and paper under supervision”, however, both came to the conclusion that this would be backward thinking (UM-News, 2023).

Figure 2. ChatGPT has left the world divided since its introduction.
Jansen and Vermeer suggested that digital literacies will also be affected because ChatGPT responses are just producing more information (UM-News, 2023). It is, therefore up to the user to learn how to tweak the system to get the right bit of information, states Jansen (UM-News, 2023). He believes that people “need a really high degree of digital literacy” to be able to use advanced AI- programs in the right manner (UM-News, 2023). Which is contrary to what is promoted by ChatGPT. There seems to be a widely accepted belief that this chatbot is accessible and usable to anyone who wants to use it. However, this seems not absolute. The concluding remarks by Jansen and Vermeer state that there is still room for improvement. As a result, they believe that ChatGPT might produce more nonsense because the user is not digitally literate enough to prompt the system (UM-News, 2023).
The problems stated by Jansen and Vermeer seem to be less harmless than what the “Godfather of deep learning” has had to say after quitting his position at Google. This is because in the case of Jansen and Vermeer any individual is able to control the problem by improving their digital literacies skills, but Hinton does not consider this to be the problem. Hinton, aka the Godfather, is 75 years old and throughout his time researching and working on neural networks and deep learning, he has gathered that AI systems such as ChatGPT are dangerous tools if they are not regulated properly (Kleinman & Vallance, 2023). This is because in AI there is a neural network that advances just as a human brain does. This means that it can constantly learn and process information, rapidly. So an AI system learns from an experience like a person would, in other words, it is deep learning (Kleinman & Vallance, 2023). Hinton concludes that the system is faster and better and therefore can take over humans' jobs and create tools that can put the globe in danger (Kleinman & Vallance, 2023). In the end, it seems that Hinton believes that the government is responsible for managing AI advancement, and he does not regard the digital literacy skills of individuals to be a necessity.
Discussion
Even though ChatGPT is viewed, on the one hand as a problematic machine that has destroyed academia and on the other hand it is considered a powerful AI system that will end the world, it is at the end of the day an unavoidable tool that is being used by the public. ChatGPT offers a great program, that supports a wide range of skills which is handy for those who need it. There is a fear that some will abuse this system for harmful acts, but others have found a way to enlighten their current lifestyle.
For example, a young digital creator named Julia Koopman has made use of AI systems by creating content that involves her asking ChatGPT what she should do for a specific task. She calls her series the “Me, Myself and AI” journey, and she showcases how AI has had a rather positive influence on her day-to-day life routine. One of her most viewed TikTok videos has brought on an intriguing but also unique aspect to what AI programs can contribute to a content creator. In the video, Julia demonstrates how she simply asked ChatGPT to solve one of the major issues for women who want to spend the whole day at a social gathering, that offers not enough public restrooms for women.
Instead of breaking her head about what to do, she went online and typed into the chatbot what women should do on a day like Kingsday when they have to use the bathroom. ChatGPT came up with the idea for her to purchase a small device that allows women to urinate while standing. Not only was she astonished by the tool, but also most people she came across and interviewed had no idea what the tool was for. At the end of the video, she made use of it and evaluated that the device worked but it was not so great. However, she considered the experience valuable.
As of now, Julia has four TikTok videos (Figure 3) where she lets ChatGPT decide what to do. And in each video, she goes about it in a similar way. She offers ChatGPT a problem and when the chatbot comes up with a solution she tries it out, and evaluates it at the end. Consequently, it is plausible to consider that AI systems have a positive influence on content creators, which offers people such as Julia, the possibility to entertain their crowds.
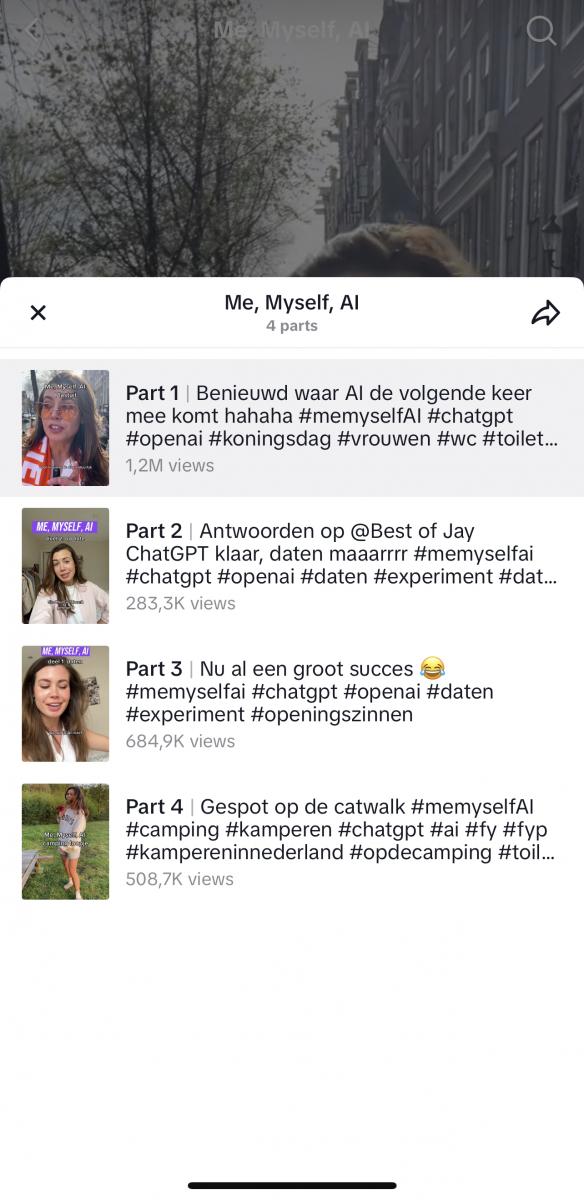
Figure 3. Series by Julia Koopman on TikTok where she has integrated AI into her daily routine.
However, on a more serious note, ChatGPT can cause also issues, for example in the academic world. While it is widely accepted in the entertainment industry, within academics ChatGPT has caused more problems than solutions. Academic intuitions have been already plagued for a long time with cheating scandals, however, the big difference here with AI systems is that the Chatbots are free and give immediate answers, which are most of the time correct but difficult to detect for professors(Mitchell, 2023). For example, a philosophy teacher, Mr Hick at a South Carolina college, has encountered a student that made use of ChatGPT (Mitchell, 2023).
He ordered his class to write a 500-word philosophy paper and the students made use of the AI system (Mitchell, 2023). Mr Hick says that the problem was not surprising since these cheating incidences happen often, but it was harder to detect this time because it is almost impossible to evaluate the input of ChatGPT (Mitchell, 2023). Mr Hick also has fears regarding the AI program's deep learning techniques (Mitchell, 2023). He believes, that ChatGPT will improve and therefore make fewer mistakes, which will make it almost completely impossible to find plagiarism on a student’s paper (Mitchell, 2023).
Conclusion
ChatGPT and the other future AI programs that are being developed have challenged the globe and how people will function in the future. In this essay, Blommaert’s (2020) theories regarding old and new media have been reviewed, and indicate that similar problems through the rise of ChatGPT have come forward. In fact, individuals have been urged to adopt their digital literacies, which can be considered rather difficult. But through Belshaw's (2014) understanding of what digital literacies are, the issues regarding ChatGPT can be tackled better. This was continuously explained through Kress's (2004) writing, which has developed the notion of multimodality within literacies and that there needs to be a clearer definition of meaning.
The articles of Maastricht University and BBC have demonstrated the particular problem of ChatGPT. Jansen and Vermeer believe that the chatbot creates nonsense and that users' digital literacies need to improve drastically before they can make use of it properly. In addition, Hinton considered the AI system to be too problematic to be put on the free market without the necessary regulations. He, therefore, argued for institutions to develop appropriate mandates.
The two examples that were illustrated near the end, have demonstrated the possible harmful and harmless input AI systems have. Julia Koopman showcased a fun and intriguing manner of using AI programs to create content, by asking random questions and using the answers for her series. But Mr Hick's experience with AI as a professor in college was less amusing compared to Julia's. This is because Mr Hick is worried that ChatGPT deep learning will make the machine undetectable and students could plagiarise without being caught.
Since AI systems are possibly unavoidable and affect the future even more over time, the only solution that could be suggested is that every individual is in need of furthering their digital literacies. This will help gatekeep the possible problems that will be encountered in the future. However, to completely denounce the program would not offer society any good, this is because technologies have overall benefited everyone's lives. It is all about regulating the devices properly and encouraging individuals to develop their digital literacy skills.
References
Artificial intelligence (AI) | Definition, Examples, Types, Applications, Companies, & Facts. (2023, May 16). Encyclopedia Britannica. https://www.britannica.com/technology/artificial-intelligence/Alan-Turin...
Belshaw, D. (2014). The Essential Elements Of Digital Literacies. Retrieved from <http://digitalliteraci.es>
Blommaert, J. (2020, June 19). Jan Blommaert on “Old new media” [Video]. YouTube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=BDRFyXkCaLo
Hughes, A. (2023). ChatGPT: Everything you need to know about OpenAI’s GPT-4 tool. www.sciencefocus.com. https://www.sciencefocus.com/future-technology/gpt-3/
Kleinman, Z. & Vallance, C. (2023, May 2). AI “godfather” Geoffrey Hinton warns of dangers as he quits Google. BBC News. https://www.bbc.com/news/world-us-canada-65452940
Kress, G. (2004). Literacy in the New Media Age. Routledge.
Mitchell, A. (2022, December, 26). Professor catches student cheating with ChatGPT: ‘I feel abject terror’. New York Post. https://nypost.com/2022/12/26/students-using-chatgpt-to-cheat-professor-...
UM-News. (2023, March 29). ChatGPT and studying-use it, don’t abuse it. Maastricht University. https://www.maastrichtuniversity.nl/news/chatgpt-and-studying-%E2%80%93-...